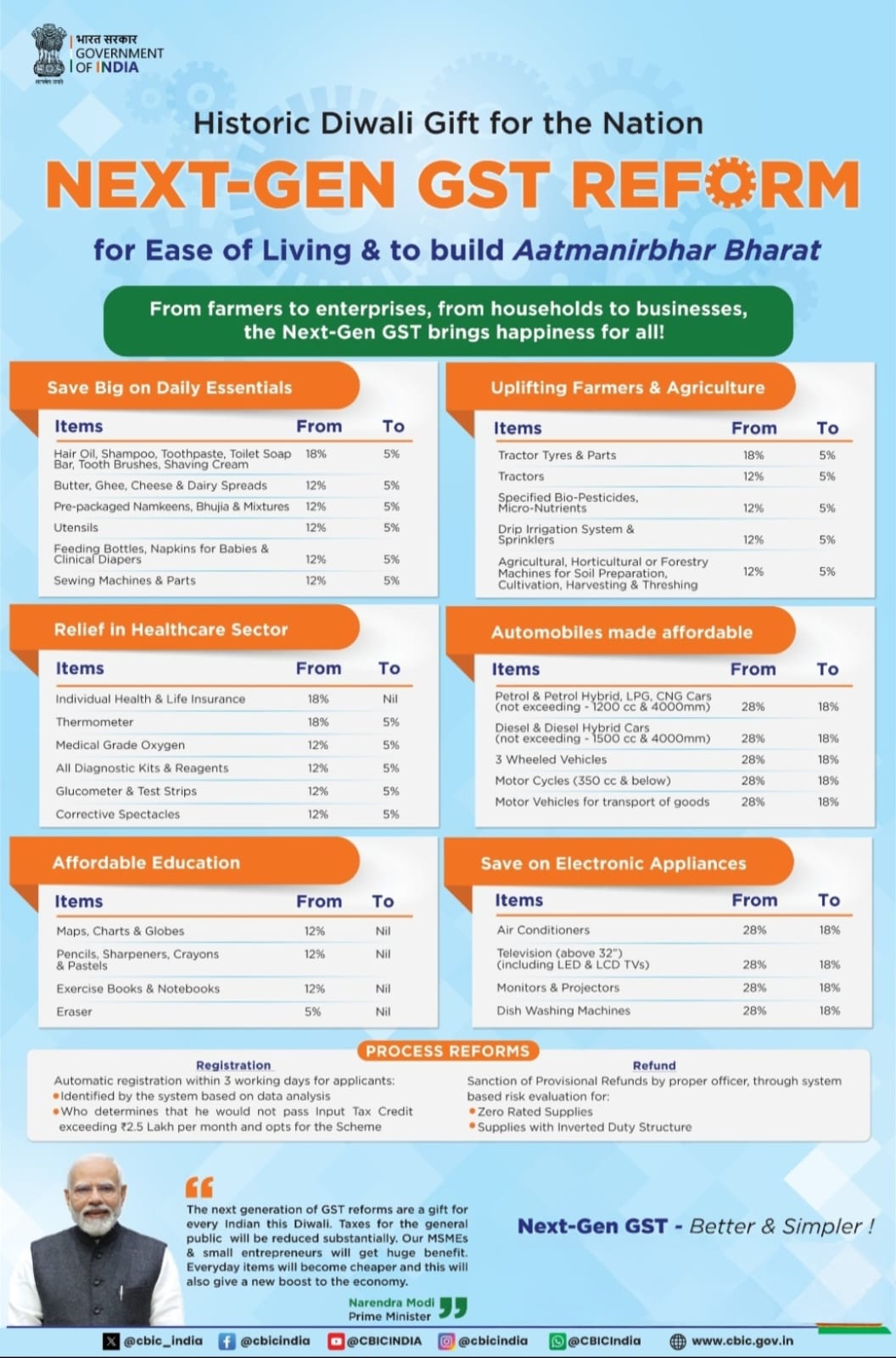
New Delhi, September 4, 2025 – In a sweeping move aimed at simplifying India’s complex indirect tax structure, the GST Council, led by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, unveiled a landmark reform on Wednesday, September 3, 2025. Key changes include shrinking the existing four GST slabs into just two—5% and 18%—while introducing a 40% “sin and luxury” tax slab for selected high-end and harmful goods.
What Changed?
- Simplified tax structure: The 12% and 28% slabs have been eliminated. Most essentials and household items now fall under 5% GST, while standard goods will attract 18%. The 40% slab targets luxury and harmful products like tobacco and high-end vehicles.
- Zero‑rated essentials: Items such as Indian breads, paneer, and ultra‑high temperature (UHT) milk are now exempt (0% GST), easing daily expenses for households
- Wider relief scope: The tax cut extends to packaged foods, personal care products, air conditioners, cars, and insurance—either taxed at 5% or fully exempt. FMCG firms like Hindustan Unilever and Nestlé are poised to benefit.
Economic and Market Impact
- The government estimates a revenue loss of ₹48,000 crore (approx. USD 5.5 billion), notably lower than earlier forecasts. Analysts expect reduced inflation (by up to 1.1 percentage point) and a boost to growth, with GDP rising by 100–120 basis points in the coming year
- Markets responded positively—Nifty gained 0.53%, Sensex rose 0.55%—with consumer and auto stocks surging. companies like Maruti, Mahindra, Britannia, and Colgate saw notable gains.
Political and Strategic Significance
- Relief to the common man: Prime Minister Modi framed these reforms as a Diwali gift, echoing his Aug 15 promise of GST rationalization before the festival. He emphasized that the changes will benefit all societal segments, from households to farmers and MSMEs.
- Cooperative federalism in focus: While supported by many states, concerns linger over fiscal compensation, especially for manufacturing-heavy states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
UPSC Relevance
- Policy Design & Implementation: This reform is a prime example of fiscal policy aiming to balance equity with efficiency—simplifying tax slabs, relieving the middle class, managing inflation, and supporting sectors like FMCG and auto.
- Economic Growth & Inflation: It illustrates the use of tax policy as a macroeconomic tool to stimulate consumption amid external trade challenges (e.g., rising U.S. tariffs) and aligns with broader economic goals of maintaining momentum through domestic demand
- Federalism & Centre‑State Relations: The compensation mechanism and states’ concerns highlight the nuances of fiscal federalism in a diverse country like India.
This GST overhaul—dubbed “Next‑Gen GST”—marks a major reform in India’s indirect taxation landscape, marrying simplification with inclusivity just ahead of the festive season.
Source : The Economic Times, Times of India
UPSC CSE MAINS PRACTICE QUESTION
GS Paper III: Indian Economy
Q2) “The recent GST slab rationalization is a step toward greater fiscal simplicity, equity, and economic growth.” Discuss the implications of the 2025 GST reforms in the context of India’s indirect tax policy. (250 words)
Q2) The introduction of a simplified GST regime with fewer slabs is expected to boost consumption-led growth in India. Analyze the macroeconomic rationale and possible challenges in implementing this reform. (250 words)
GS Paper II: Governance & Polity
Q3) Cooperative federalism remains central to GST Council decisions. In light of the recent GST reform, evaluate the role of the GST Council in balancing Centre-State fiscal interests. (250 words)